On Jan. 25, 2018, dozens of private jets descended on Palm Springs International Airport. Some of the richest people in the country were arriving for the annual winter donor summit of the Koch network, the political organization founded by libertarian billionaires Charles and David Koch. A long weekend of strategizing, relaxation in the California sun and high-dollar fundraising lay ahead.
Just after 6 p.m., a Gulfstream G200 jet touched down on the tarmac. One of the Koch network’s most powerful allies was on board: Supreme Court Justice Clarence Thomas.
During the summit, the justice went to a private dinner for the network’s donors. Thomas has attended Koch donor events at least twice over the years, according to interviews with three former network employees and one major donor. The justice was brought in to speak, staffers said, in the hopes that such access would encourage donors to continue giving.
That puts Thomas in the extraordinary position of having served as a fundraising draw for a network that has brought cases before the Supreme Court, including one of the most closely watched of the upcoming term.
Thomas never reported the 2018 flight to Palm Springs on his annual financial disclosure form, an apparent violation of federal law requiring justices to report most gifts. A Koch network spokesperson said the network did not pay for the private jet. Since Thomas didn’t disclose it, it’s not clear who did pay.
Thomas’ involvement in the events is part of a yearslong, personal relationship with the Koch brothers that has remained almost entirely out of public view. It developed over years of trips to the Bohemian Grove, a secretive all-men’s retreat in Northern California. Thomas has been a regular at the Grove for two decades, where he stayed in a small camp with real estate billionaire Harlan Crow and the Kochs, according to records and people who’ve spent time with him there.
A spokesperson for the Koch network, formally known as Stand Together, did not answer detailed questions about his role at the Palm Springs events but said, “Thomas wasn’t present for fundraising conversations.”
“The idea that attending a couple events to promote a book or give dinner remarks, as all the justices do, could somehow be undue influence just doesn’t hold water,” the spokesperson said in a statement.
“All of the sitting Justices and many who came before them have contributed to the national dialogue in speeches, book tours, and social gatherings,” the statement added. “Our events are no different. To claim otherwise is false.”
In a series of stories this year, ProPublica reported that Thomas has accepted undisclosed luxury travel from Crow and a coterie of other ultrawealthy men. Crow also purchased Thomas’ mother’s home and paid private school tuition for the child Thomas was raising as his son. Thomas has said little in response. In a statement earlier this year, he said that Crow is a close friend whom he has joined on “family trips.” He has also argued that he was not required to disclose the free vacations. Thomas did not respond to questions for this story.
The code of conduct for the federal judiciary lays out rules designed to preserve judges’ impartiality and independence, which it calls “indispensable to justice in our society.” The code specifically prohibits both political activity and participation in fundraising. Judges are advised, for instance, not to “associate themselves” with any group “publicly identified with controversial legal, social, or political positions.”
But the code of conduct only applies to the lower courts. At the Supreme Court, justices decide what’s appropriate for themselves.
“I can’t imagine — it takes my breath away, frankly — that he would go to a Koch network event for donors,” said John E. Jones III, a retired federal judge appointed by President George W. Bush. Jones said that if he had gone to a Koch summit as a district court judge, “I’d have gotten a letter that would’ve commenced a disciplinary proceeding.”
“What you’re seeing is a slow creep toward unethical behavior. Do it if you can get away with it,” Jones said.
The Koch network is among the largest and most influential political organizations of the last half century, and it’s underwritten a far-reaching campaign to influence the course of American law. In a case the Supreme Court will hear this coming term, the justices could give the network a historic victory: limiting federal agencies’ power to issue regulations in areas ranging from the environment to labor rights to consumer protection. After shepherding the case to the court, Koch network staff attorneys are now asking the justices to overturn a decades-old precedent. (Thomas used to support the precedent but flipped his position in recent years.)


Two years ago, one of the network’s groups was the plaintiff in another Supreme Court case, which was about nonprofits’ ability to keep their donors secret. In that case, Thomas sided with the 6-3 conservative majority in the Koch group’s favor.
Charles Koch did not respond to detailed questions for this story. David Koch died in 2019.
The Koch network is an overlapping set of nonprofits perhaps best known for its work helping cultivate the Tea Party movement in the Obama years. Recently rebranded as Stand Together, the network includes the powerful Americans for Prosperity Action, which spent over $65 million supporting Republican candidates in the last election cycle.
Though Charles Koch is one of the 25 richest people in the world, worth an estimated $64 billion, he raises money from other wealthy people to amplify the network’s reach. The network brought in at least $700 million in 2021, the most recent year for which data is available. It has more than 1,000 employees who, on paper, work for different groups.
But for all its complexity, the network is a centralized operation, staffers said. Many of the groups occupy the same buildings in Arlington, Virginia, and share leadership and often staff. Many of the donations go into a central pot, from which hundreds of millions of dollars are disbursed to the smaller groups focused on various political and social concerns, according to tax filings and former employees.
For decades, the Kochs have held deep antipathy to government regulation. When Charles Koch’s brother David ran for vice president on the Libertarian Party ticket in 1980, the party platform called for abolishing the Environmental Protection Agency, the Department of Energy and the Food and Drug Administration.
Every winter, the network holds its marquee fundraising event in the Coachella Valley in Southern California. Hundreds of donors fly in to learn how their money is being spent and plan for the coming year. Former staffers describe an emphasis on preventing leaks that bordered on obsession. The network often rents out an entire hotel for the event, keeping out eavesdroppers. Documents left behind are methodically shredded. One recent attendee recalled Koch security staff in a golf cart escorting their Uber driver out of the hotel to make sure he left. The former staffers spoke on the condition of anonymity because they feared retaliation.
To score an invite to the summit, donors typically have to give at least $100,000 a year. Those who give in the millions receive special treatment, including dinners with Charles Koch and high-profile guests. Doling out access to powerful public officials was seen as a potent fundraising strategy, former staffers said. The dinners’ purpose was “giving donors access and giving them a reason to come or to continue to come in the future,” a former Koch network executive told ProPublica.

Thomas has attended at least one of the dinners for top-tier donors, according to a donor who attended and a former high-level network staffer.
“These donors found it fascinating,” said another former senior employee, recounting a Thomas appearance at one summit where the justice discussed his judicial philosophy. “Donors want to feel special. They want to feel on the inside.”
A former fundraising staffer for the Koch network said the organization’s relationship with Thomas was considered a valuable asset: “Offering a high-level donor the experience of meeting with someone like that — that’s huge.”
Many details about Thomas’ role at the summits, including the specifics of his remarks, remain unclear. The network spokesperson declined to answer if Thomas’ appearances were ever tied to a specific initiative or program.
Thomas’ appearances were arranged with the help of Leonard Leo, the Federalist Society leader, according to the former senior network employee. “Leonard was the conduit who would get him,” the former employee said. During one summit, Thomas gave a talk with Leo in an interview format, the donor recalled.
“Justice Thomas attends events all over the country, as do all the Justices, and I was privileged to join him,” Leo said in a statement in response to questions about the Koch donor events. “All the necessary due diligence was performed to ensure the Justice’s attendance at the events was compliant with all ethics requirements.”
While attending the donor events would likely violate the lower courts’ prohibition on fundraising, experts said, the Supreme Court has a narrow internal definition of a fundraiser: an event that raises more money than it costs or where attendees are explicitly asked for money while the event’s happening.
On the Thursday before the January 2018 summit in Palm Springs, Thomas flew there on a chartered private jet, according to records reviewed by ProPublica. Four days later, the plane flew to an airport outside Denver, where Thomas appeared at a ceremony honoring his former clerk, federal Judge Allison Eid. The next day, it flew back to northern Virginia where Thomas lives.
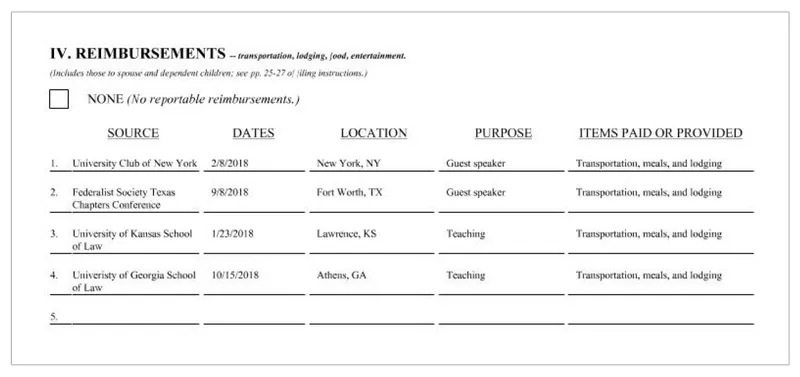
Thomas’ financial disclosure for that year contains two speaking engagements: one in New York City and another at a Federalist Society conference in Texas. His trip to the Koch event in California is not on the form.
For the event that year, the Koch network rented out the Renaissance Esmeralda Resort and Spa. On the main stage, donors heard from Hall of Fame NFL cornerback Deion Sanders, who was working with the Kochs on anti-poverty programs in Dallas. Another speaker delivered a report card on the group’s political wins large and small: “repealed voter-approved donor disclosure initiative”; “retraction of mining & environmental overreach”; “stopped Albuquerque paid sick leave mandate.”
During the event, the group announced a new initiative focused on getting conservatives on the Supreme Court and the federal bench. The network, which had already given millions of dollars to Leo’s Federalist Society, planned to mobilize its activists and buy advertisements to push senators to vote for President Donald Trump’s judicial nominees. They appointed a former employee of Ginni Thomas, the justice’s wife, to lead the effort.
The first glimpse of Thomas’ connection to the network came more than a decade ago. In 2010, reporters obtained an invitation sent to potential Koch donors that mentioned Thomas had been “featured” at one of the network’s previous summits.
After critics called for more information about Thomas’ attendance, the Supreme Court press office downplayed the episode. A court spokesperson acknowledged Thomas had been in the Palm Springs area during the Kochs’ January 2008 summit. However, she said he was there to talk about his memoir at a Federalist Society dinner that was separate from the donor summit but was also sponsored by Charles Koch. She added that Thomas made a “brief drop-by” at the network summit that year but said he “was not a participant.” (Thomas disclosed the 2008 Palm Springs trip as a Federalist Society speech.)
In the 15 years since, the Koch network has left a deep imprint on American society. Its advocacy is credited with helping stamp out Republican Party support for combating climate change, once an issue that drew bipartisan concern. The “full weight of the network” was thrown behind passing the 2017 Trump tax cut, securing a windfall for the Kochs and their donors. And the upcoming Supreme Court term could bring the network a victory it has pursued for years: overturning a major legal precedent known as Chevron.
While most Americans aren’t familiar with the 1984 case Chevron v. NRDC, it’s one of the Supreme Court’s most-cited decisions. Legal scholars sometimes mention it in the same breath as Brown v. Board of Education and Roe v. Wade. In essence, Chevron is about government agencies’ ability to issue regulations. After a law is enacted, it’s generally up to agencies across the government to make detailed rules putting it into effect. The Chevron decision said courts should be hesitant to second-guess the agencies’ determinations. In the years that followed, judges cited Chevron in upholding rules that protect endangered species, speed up the approval process for new cellphone towers and grant benefits to coal miners suffering from black lung.
The Koch network has challenged Chevron in the courts and its lobbyists have pushed Congress to pass a law nullifying the decision. It has also provided millions of dollars in grants to law professors making the case to overturn it.
The network’s position has become increasingly popular in recent years. Once broadly supported by academics and judges on the right, Chevron is now anathema to many in the conservative legal movement. And there’s no more prominent convert than Thomas.
In 2005, Thomas wrote the majority opinion in a case that expanded Chevron’s protections for government agencies. Ten years later, he was openly questioning the doctrine. Then in 2020, Thomas renounced his own earlier decision, writing that he’d determined the doctrine is unconstitutional after all — a rare reversal for a justice with a reputation for being unmovable in his views.
By last year, Koch network strategists sensed that victory could be at hand. During an internal briefing for network staff, Jorge Lima, a senior vice president at Americans for Prosperity, said the Supreme Court seemed primed to radically change its approach to the issue. The network was trying to find cases that could bring about major changes in the law, according to a video of the meeting obtained by the watchdog group Documented. “We’re doubling down on this strategy,” Lima told the crowd.
Several months later, the Supreme Court announced it would take up a case, Loper Bright Enterprises v. Raimondo, in which Koch network staff attorneys represent the plaintiffs. If Thomas and his colleagues side with them this coming term, Chevron will be overturned once and for all.
Without Chevron, “any place you would need regulation to address a pressing social problem, it’s going to be more costly to get it, harder to implement it and it’s not going to go as far,” said Noah Rosenblum, a professor at New York University School of Law.
“Loper Bright is a case seeking to restore one of the core tenets of our democracy: that Congress, not the administrative agency, makes the laws,” the Koch network spokesperson said.
Ethics experts said Thomas’ undisclosed ties to the Koch network could call his impartiality in the case into doubt. This sort of potential conflict is why the judiciary has rules against both political activity and fundraising, they said. “Parties litigating in the court before Justice Thomas don’t know the extent of Thomas’ relationship with the parties on the other side,” said James Sample, a Hofstra University law professor who studies judicial ethics. “You have to be pretty cynical to not think that’s a problem.”
The Supreme Court itself said in a recent statement to The Associated Press that “justices exercise caution in attending events that might be described as political in nature.” But unlike with lower court judges, there is no formal oversight of the justices.
Two decades ago, Justice Ruth Bader Ginsburg delivered the opening remarks at a lecture cosponsored by the NOW Legal Defense and Education Fund, a women’s rights group that filed friend-of-the-court briefs at the Supreme Court. It was a public event co-sponsored by the New York City Bar Association. But some judicial ethics experts criticized the justice for affiliating herself with an advocacy group.
Thirteen Republican lawmakers, including Mike Pence and Marsha Blackburn, who now sits on the Senate Judiciary Committee, went further, calling on Ginsburg to recuse herself from any future cases related to abortion. The justice brushed off the criticism: “I think and thought and still think it’s a lovely thing,” she said of the lecture series. (Ginsburg died in 2020.)
Charles and David Koch’s access to Thomas has gone well beyond his participation in their donor events. For years, the brothers had opportunities to meet privately with Thomas thanks to the justice’s regular trips to the Bohemian Grove, an all-male retreat that attracts some of the nation’s most influential corporate and political figures. Thomas has been a regular at the Grove for 25 years as Harlan Crow’s guest, according to internal documents and interviews with dozens of members, other guests and workers at the retreat.

“What we’re seeing emerge is someone who is living his professional life in a way that’s seeing these extrajudicial opportunities as a perk of the office,” said Charles Geyh, a judicial ethics expert at Indiana University law school. Judges can have social lives, he said, and there are no clear lines for when a social gathering could pose a problem. But the confluence of powerful political actors and undisclosed gifts puts Thomas’ trips far outside the norm for judges’ conduct, Geyh said: “There’s a culture of impartiality that’s really at risk here.”
The Grove is an exclusive, two-week party held in the Sonoma County redwoods every July. A member or his guest can wander from the Grove’s shooting range to a lecture by Blackwater founder Erik Prince, or from a mint julep party to a performance by the Grove’s symphony orchestra. Wine, sometimes at $500 a bottle, flows freely, and late at night, members consume clam chowder and chili by the gallon. More than one attendee recalled walking outside in the morning to find a former cabinet secretary who fell asleep drunk in the grass.
There’s a saying among the Bohemians, as the club’s members call themselves: The only place you should be publicly associated with the Grove is in your obituary. That privacy is paramount, members said, in part to allow the powerful to speak freely — and party — without worrying about showing up in the press. Only designated photographers are allowed to take pictures. Cellphones are strictly forbidden.


Members typically must pay thousands of dollars to bring a guest. Several people ProPublica spoke to said that before the pandemic, they saw Thomas there just about every year. ProPublica was able to confirm six trips Thomas took to the retreat that he didn’t disclose. Flight records suggest Crow has repeatedly dispatched his private jet to Virginia to pick up Thomas and ferry him to the Sonoma County airport and back, usually for a long weekend in the middle of the Grove festival.
“I was taken with how comfortable he was in that environment and how popular,” a person who stayed in the same lodge as Thomas one year said. “He holds court there.”
In response to questions about his travel to the Grove with Thomas, Crow said Thomas is “a man of incredible integrity” and that he’s never heard the justice “discuss pending legal matters with anyone.” Neither Crow nor Thomas responded to questions about whether the justice reimbursed him for the trips.
(Other justices have Grove connections too. The mid-20th-century Chief Justice Earl Warren was a member. Among modern justices, Thomas appears to have been the most frequent guest. Justice Antonin Scalia, who died in 2016, attended many years ago. Justice Stephen Breyer went in 2006; he told ProPublica he was the guest of his brother and that to the best of his memory, he paid his own way. Justice Anthony Kennedy went at least twice before he retired. Kennedy, who did not respond to a request for comment, did not disclose the trips. It’s unclear if he needed to because his son is a member and gifts from family don’t need to be reported.)

The Grove is broken up into more than 100 “camps,” essentially adult fraternity houses where the same group of men stay together year after year. Hill Billies was George H. W. Bush’s camp. Nancy Pelosi’s husband has been a longtime member of Stowaway. Thomas stays with Crow at a camp called Midway.
One of the ritzier camps, Midway employs a staff of cooks and personal valets and boasts an extensive wine cellar. The men sleep in private cabins that zigzag up a hillside. Known for its Republican leanings, Midway has a string of superrich political donors as members, including an heir to the Coors beer empire and the owner of the New York Jets. Charles Koch is an active member, as was his brother David. It’s not clear if Thomas has ever been the guest of a member other than Crow.

During the annual retreats, the Kochs often discussed political strategy with fellow guests, according to multiple people who’ve spent time with them at Midway. A few years ago, Brian Hooks, one of the leaders of their political network, was a guest at the camp the same weekend Thomas was there. A former Midway employee recalled the brothers discussing super PAC spending during the Obama years and complaining about government regulation.
“Chevron was one of the big things the Koch brothers were interested in,” the former employee said. He did not remember if Thomas was present for any of the discussions of the doctrine.
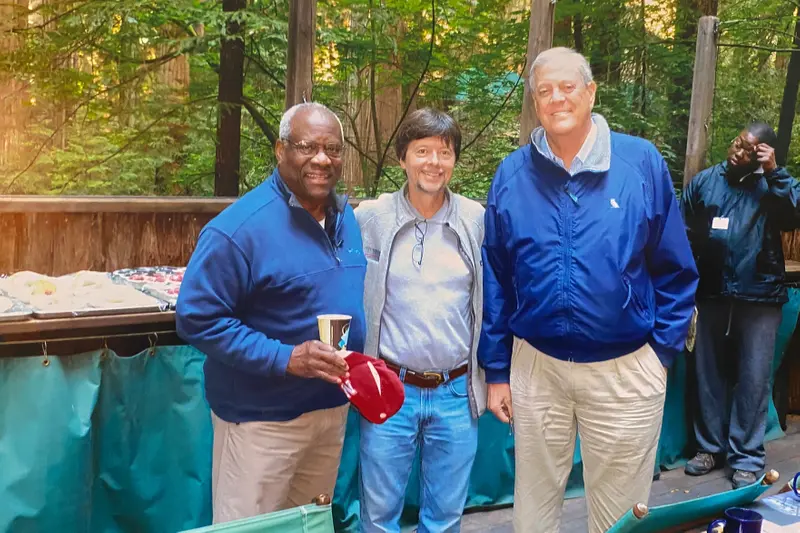
But Thomas and the Kochs developed a bond over their years at the retreat, according to five people who spent time with them there. They discussed politics, business and their families. They often sat together at meals and sat up talking at night at the lodge. A photo obtained by ProPublica captures Thomas and David Koch smiling on Midway’s deck. David’s windbreaker features an owl insignia, the symbol of the club.
One tradition at Midway is a lecture series, often held beneath the redwoods on the camp’s deck. The weekend Thomas was there in July 2016, the Midway schedule featured a talk from Henry Kissinger and another by Michael Bloomberg and Arthur Brooks, then president of the conservative think tank the American Enterprise Institute. Over breakfast Friday morning, the author Bjorn Lomborg delivered a lecture on climate change. Lomborg has for years argued the threat of global warming is overstated, saying that rising temperatures will actually save lives.
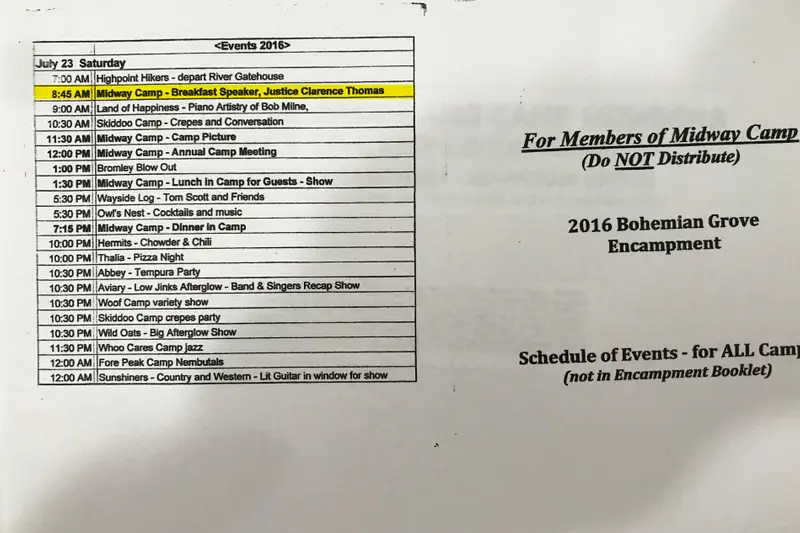
Thomas spoke that year as well. He talked about his friend Justice Scalia, who had recently died, according to a person who attended. Scalia, a conservative luminary, had been a prominent advocate for the Chevron doctrine, but Thomas said he believed his colleague was coming around to Thomas’ revised view on it before his death.
Thomas didn’t explain what he meant by that. “It was an aside,” the person said, “like he assumed most of the people in the room knew his position.”
Do you have any tips on the Supreme Court? Josh Kaplan can be reached by email at [email protected] and by Signal or WhatsApp at 734-834-9383. Justin Elliott can be reached by email at [email protected] or by Signal or WhatsApp at 774-826-6240.












